Urinary incontinence is a common health condition that involves the loss of bladder control and involuntary leakage of urine. It can vary in severity, from occasionally losing a few drops of urine to leaking a substantial amount several times each day.
Urinary incontinence can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, particularly as the condition can pose embarrassing situations in social or public environments. In most cases, urinary incontinence occurs as a result of an underlying health condition, which can be treated and lead to a dramatic improvement in symptoms.
The urinary system
The bladder plays a central role in the complex process of urination, as it stores the urine until it is ready to be excreted via the urethra. There are several nerves and muscles involved in this process, along with the brain and central nervous system (CNS) that control these actions.
The detrusor muscles in the bladder compose the sac used to store urine and contract to squeeze urine out. The sphincter muscles are located at the bottom of the bladder and are naturally contracted to hold the “gate” of the bladder closed and keep urine inside the bladder. When the sphincter muscles relax and the detrusor muscles contract simultaneously, urine is pushed down to be excreted via the urethra.
The CNS is particularly important, as it is responsible for sending messages to the relevant muscles to urinate when needed. When this fails, either due to a fault in the CNS or with particular muscles, urinary incontinence may occur.
Types of urinary incontinence
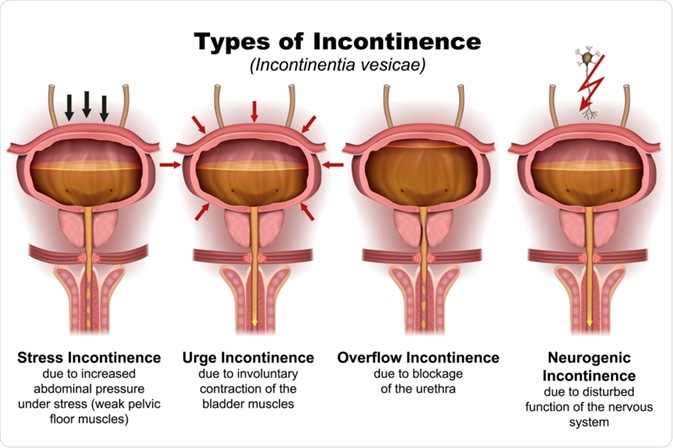
Image Credit: medicalstocks / Shutterstock.com
There are five different types of urinary incontinence, as outlined below.
- Stress incontinence occurs when there is a leakage of urine due to pressure on the abdomen, like when coughing, laughing, or lifting something heavy. This form of urinary incontinence is more common in women and is often caused by circumstances that lead to the weakening of pelvic muscles, such as childbirth or local surgery.
- Urge incontinence involves the sudden need to urinate, such that the individual often does not have enough time to reach a toilet. This is particularly common in elderly people and is often caused by a urinary tract infection (UTI) or overactive bladder.
- Overflow incontinence is when small amounts of urine are leaked due to an overfilled bladder. Patients often have difficulty voiding completely, which affects more men, in particular, who are affected by an enlarged prostate.
- Functional incontinence refers to leaking of urine due to another condition leading to difficulty reaching the toilet in time, rather than a problem with the urinary system. Diseases that make mobility difficult, such as arthritis, may cause this type of incontinence.
- Mixed incontinence is a combination of several types of incontinence. There are often multiple causes to be addressed in the appropriate management of this condition.
Management
When deciding the best course of action to treat urinary incontinence, it is important to consider the cause of the condition. This will often help to identify possible causes and present ways to improve both the primary condition and the symptoms of urinary incontinence.
Pelvic floor muscles are the muscles used to stop the flow of urination voluntarily. Kegel exercises can help to strengthen these muscles and have been shown to improve the symptoms of many people who suffer from urinary incontinence. Overall, kegel exercises have been found to be particularly successful in the treatment of stress incontinence.
Some medications are also able to target the muscles responsible for the process of urination and are able to help control the urine flow. If there is a structural abnormality that is causing the symptoms, surgery may be beneficial to correct the anatomy of the urinary system and improve the condition.
References
Further Reading